Autosomal recessive
An inheritance pattern in which a person must inherit two copies of an abnormal gene (one from each parent) in order to develop the disease. If two individuals each carry one copy of an abnormal gene, then each child born to these two parents will have a 25% chance of receiving 2 copies of the abnormal gene and as a result, inherit the disease. Cystic fibrosis is an example of an autosomal recessive disease.
Related Links
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance — National Eye Institute
Autosomal recessive eye and brain anomalies: Warburg syndrome. – PubMed – NCBI
OMIM Entry – # 216820 – COLOBOMA, OCULAR, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE
PID UK – Autosomal recessive inheritance
Autosomal recessive eye and brain anomalies: Warburg syndrome – ScienceDirect
Autosomal recessive congenital stationary night blindness – Genetics Home Reference – NIH
Genetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked Recessive, Mitochondrial Disease — Stomp On Step1
autosomal recessive – Eye on the Cure
Related Videos
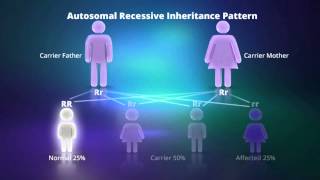
What is Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
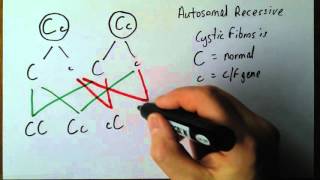
Genetics 4 Autosomal recessive disorders

Autosomal Recessive Diseases
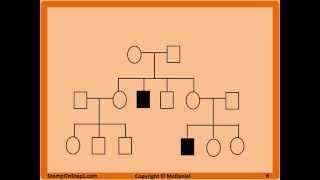
Pedigrees Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Autosomal Dominant Recessive X-Linked Mitocondrial
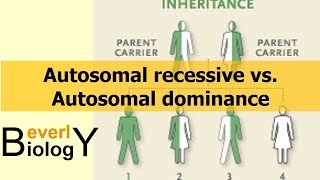
Autosomal Recessive vs. Autosomal Dominance
Autosomal Recessive Disorders

Autosomal Recessive Pedigree

Autosomal Recessive Inheritance - Genetics
-
What is Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
-
Genetics 4 Autosomal recessive disorders
-
Autosomal Recessive Diseases
-
Pedigrees Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Autosomal Dominant Recessive X-Linked Mitocondrial
-
Autosomal Recessive vs. Autosomal Dominance
-
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
-
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
-
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance - Genetics
